Understanding open interest is crucial in the world of finance, mainly when trading futures and options. Open interest indicates the overall quantity of active agreements for a particular financial instrument at any given point in time.
A futures contract entails an agreement between two parties to purchase or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified future date. Open interest measures the total number of contracts that remain outstanding, as opposed to trading volume, which tracks the total number of contracts traded during a specific time frame.
Open interest serves as a crucial measure that traders and analysts rely on to evaluate market sentiment and predict forthcoming price fluctuations. The core concept behind open interest is that it provides insights into the overall market activity and potential future developments. When open interest decreases, it may indicate a negative trend. Still, when open interest increases, it suggests a positive trend with developing interest in the market and the possibility of long-term price movements.
Considerations About the Open Market’s Impact on Market Direction
Open interest can provide valuable insights into the market’s direction, allowing traders to gain valuable perspectives from both bullish and bearish scenarios.
The growing open interest and upward movement in prices indicate a robust trend and potential for further upward momentum, suggesting a positive outlook. This alignment reinforces confidence in the overall optimistic outlook and signifies a shared agreement among market participants.
Conversely, a bearish scenario arises when there is a rise in open interest despite prices falling, indicating a potential continuation of the downward trend. This correlation suggests continuous selling pressure and traders’ consensus on the bleak forecast.
Analyzing changes in open interest is essential for identifying potential shifts in market trends. For example, a discrepancy where prices increase but open interest decreases may indicate a decline in bullish backing and potentially foreshadow a reversal.
Similarly, when prices drop, and open interest decreases, it could suggest a weakening bearish pattern and the possibility of a turnaround in the upward direction. Open interest serves as a critical indicator that trend reversal-focused traders often rely on to anticipate shifts in market sentiment and adjust their strategies for more informed trading choices.
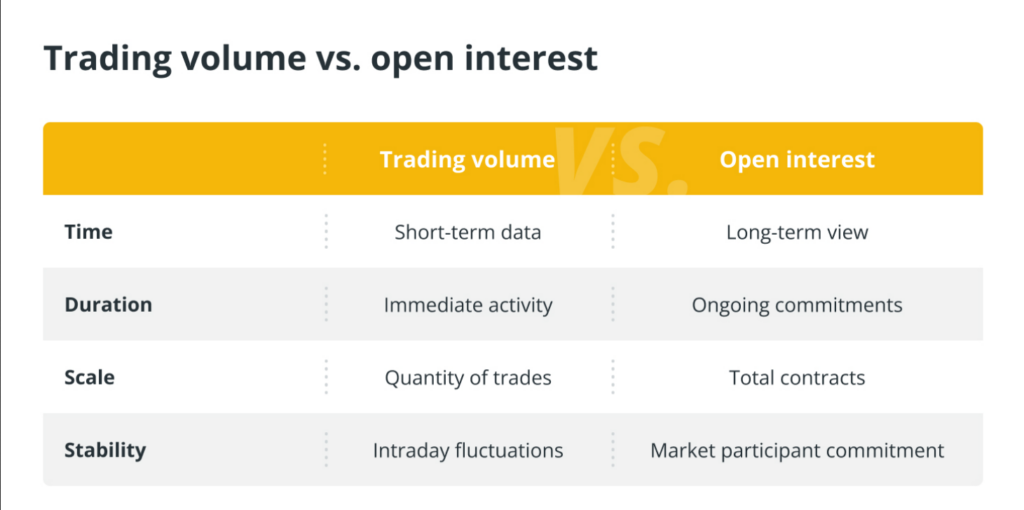
Comparing Open Interest to Trading Volume
Trading volume and open interest are both crucial indicators in financial markets, but they provide different insights into market activity.
The overall quantity of shares or contracts exchanged during a specific timeframe, or trading volume, reflects the extent of buying and selling that took place within that duration. It doesn’t differentiate between new and current investments; instead, it provides valuable information about the market’s liquidity and promptness.
On the other hand, open interest reflects the total number of contracts that remain active in the market, indicating the collective obligations of all traders. Unlike the total trading volume, open interest only considers contracts that have not yet been fulfilled through delivery or offset by a counter-deal.
Analysis of Open Interest Strategies as a Basis for Strategy
Examining open interest is crucial for traders as it provides valuable information about market sentiment and potential trend movements, serving as a basis for different trading strategies.
A commonly employed strategy involves utilizing open interest to corroborate or question established price patterns. When prices are on the rise and there is a surge in open interest, the trend is likely to persist. Conversely, a decrease in open interest may indicate diminishing backing for the pattern if prices are increasing.
Another strategy is to monitor changes in open interest and fluctuations in pricing closely. Discrepancies marked by open interest going against prices suggest a potential shift in the trend. For instance, increasing costs, when accompanied by decreasing open interest, might indicate that the current upward pattern is losing momentum.
In addition, traders often combine open interest with other technical indicators to improve their decision-making process. By combining open-interest research with various analytical tools like momentum indicators or moving averages, traders can gain a more holistic understanding of market conditions. This, in turn, enables them to identify the most favorable trading opportunities.
The Restrictions Placed on Open Interest for Cryptocurrency Futures
The accurate representation of the crypto futures market may be partially captured by open interest, as it can be challenging to differentiate between new activity and closures. Additionally, the presence of volatility and the possibility of underrepresented institutional positions further complicate the picture.
Open interest alone may not provide a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. Distinguishing between fresh market activity and position closures can pose a challenge, as alterations in open interest can stem from both new positions and offsetting trades.
In addition, the natural unpredictability of the cryptocurrency market can lead to sudden and unpredictable fluctuations in open interest, potentially undermining its reliability as a sole indicator. In addition, the data on open interest may not accurately represent the extent of significant positions held by organizational competitors, nor does it offer insights into the scale of individual positions.
In the ever-evolving realm of cryptocurrency futures trading, traders and analysts often merge open interest evaluation with additional technical indicators to navigate these limitations and acquire a more comprehensive comprehension of market conditions.


